A 5.2 GHz, 0.5 mW RF powered wireless sensor with dual on-chip antennas for implantable intraocular pressure monitoring
About
Mohamed Arsalan, et al., "A 5.2 GHz, 0.5 mW RF powered wireless sensor with dual on-chip antennas for implantable intraocular pressure monitoring." In 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (MTT), 2013, 1.
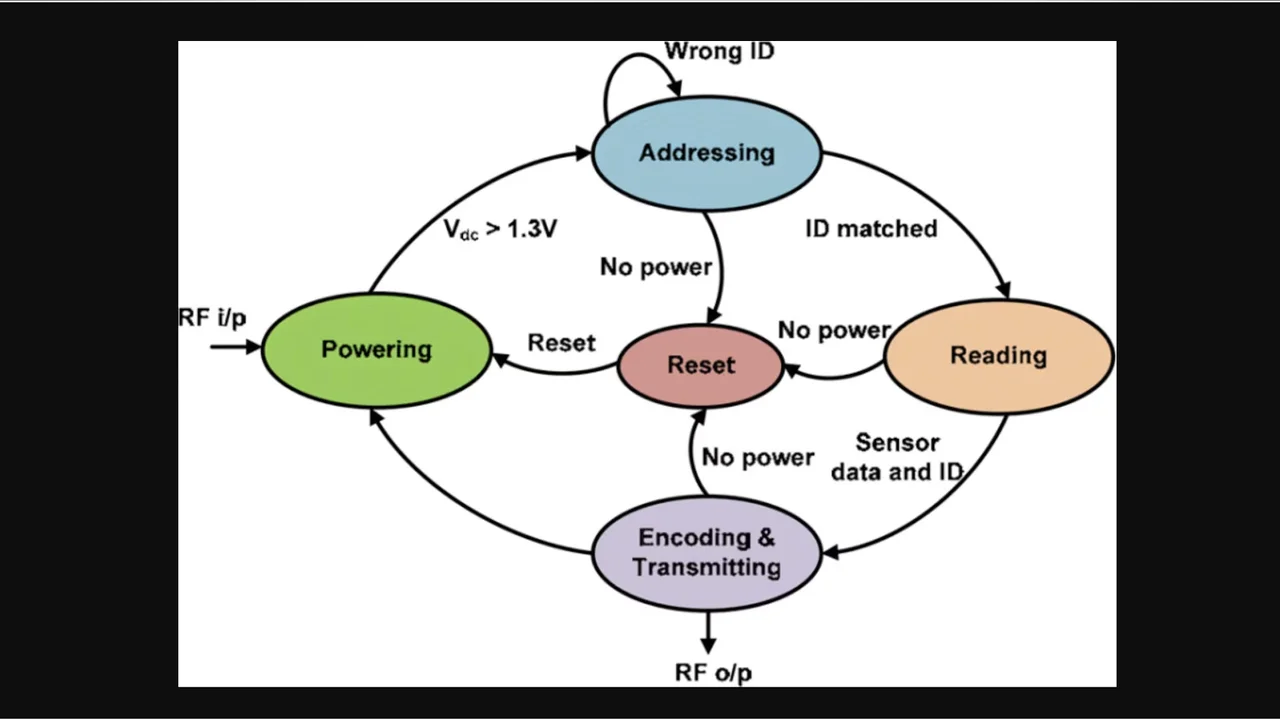
For the first time a single chip implantable wireless sensor system for Intraocular Pressure Monitoring (IOPM) is presented. This system-on-chip (SoC) is battery-free and harvests energy from incoming RF signals. The chip is self-contained and does not require external components or bond wires to function. This 1.4mm 3 SoC has separate 2.4GHz-transmit and 5.2GHz-receive antennas, an energy harvesting module, a temperature sensor, a 7-bit TIQ Flash ADC, a 4-bit RFID, a power management and control unit, and a VCO transmitter. The chip is fabricated in a standard 6-metal 0.18μm CMOS process and is designed to work with a post-processed MEMS pressure sensor. It consumes 513μW of peak power and when implanted inside the eye, it is designed to communicate with an external reader using on-off keying (OOK).